As the textile industry strives to meet growing demands for sustainability and efficiency, innovative techniques are becoming increasingly important. The dope dyeing process represents an up-and-coming innovation aimed at addressing these requirements. This method not only offers significant environmental benefits but also enhances the durability and quality of textiles. By integrating colour directly into the fibre during production, dope dyeing reduces resource consumption and pollution while delivering superior products.
Definition of Dope Dyeing
Dope dyeing, also known as solution dyeing or mass coloration, is a process where the dye is added to the polymer solution or dope before the fibre is extruded. The term “dope” refers to the chemical solution used in the dyeing process. When the dye is combined with the liquid polymer, it integrates into the fibre, maintaining the colour’s vibrancy and preventing it from fading. Unlike traditional fabric dyeing methods, where the dye is applied after the fabric is woven or knitted, dope-dyed yarn is coloured during the manufacturing process of the yarn. This means that the dye is added to the liquid polymer solution before it is extruded into fibres, resulting in a colour that is integral to the fibre itself.
Dope-dyeing Process:
Dope dyeing is commonly used for synthetic fibers such as polyester, nylon, and polypropylene as they are difficult to dye, unlike other fibers. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps involved:
1- Masterbatch Preparation: The first step is to create a concentrated colorant mixture known as a masterbatch. This masterbatch combines the desired dye with the polymer resin used to make synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon, or polypropylene.
2- Melting and Mixing: The polymer chips are melted down and then precisely blended with the pre-prepared masterbatch. This ensures uniform color distribution throughout the molten polymer solution, often referred to as “dope.”
3- Spinning: The colored dope is pushed through a spinneret, a device with small holes that determine the size of the resulting fibers. As the liquid comes out of the spinneret, it cools and becomes solid, creating continuous filaments.
4- Yarn Formation: The fibers are then pulled, stretched, and possibly twisted together to make the final yarn. This yarn will have the same color all the way through.
5- Fabric construction: The yarn that has been dyed is then processed into the final form of the textile by weaving, knitting, or other methods.
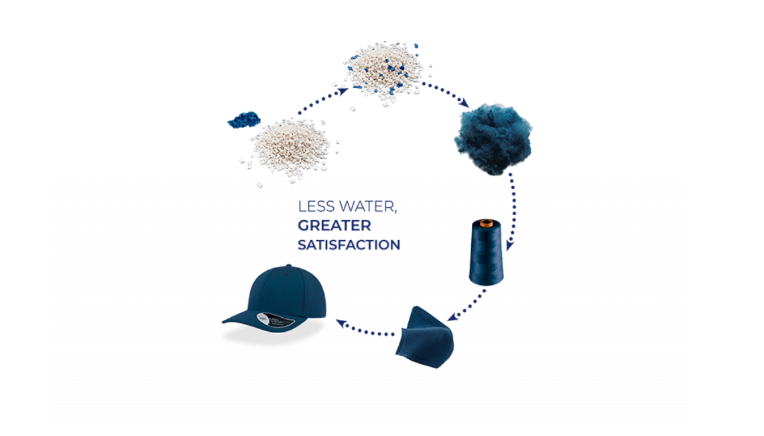

Distinction from Traditional Dyeing Methods:
The dope-dyeing method is quite different from traditional fabric dyeing approaches. Typically, in Traditional processes, the fabric is woven or knitted first and then undergoes separate dyeing procedures. This frequently entails immersing the fabric in large vats of water with dyes, leading to greater water consumption, extensive chemical washing, and energy usage.
Unlike traditional methods Dope-dyed fabric, incorporates the dye into the fibre during the initial manufacturing stage, eliminating the need for additional dyeing processes. This innovative approach provides several benefits, including better colourfastness, reduced water and chemical usage, and a more sustainable manufacturing process.
Types of Dope Dyeing:
There are primarily two types of dope dyeing based on the material used:
1- Dope Dyeing of Synthetic Fibers:
Synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon, and acrylic can be dope dyed by adding dye to the polymer before fiber formation, resulting in uniformly colored fibers.
2- Dope Dyeing of Regenerated Cellulosic Fibers:
- Viscose: Dye is added to the cellulose xanthate solution before it is regenerated into fibres.
- Lyocell: Dye is added to the cellulose solution before it is extruded and regenerated into fibers.
Advantages of dope-dyed Fabric:
Improved Colour Uniformity:
Dope dyeing ensures that the color of the yarn is consistent throughout, removing variations that can happen with traditional batch dyeing. This consistency means that manufacturers and consumers can expect reliable and predictable color results.
Colour Fastness and Fading:
Dope-dyed fabric is known for its exceptional colourfastness, remaining vibrant and resistant to fading even under harsh conditions. The fabric exhibits remarkable resistance to sunlight, washing, and exposure to chemicals, making it ideal for long-lasting and fade-resistant products such as outdoor furniture, automotive upholstery, and apparel.
Durability:
Dope-dyed fabric’s durability, strength, and colour stability are well-known. During manufacturing, the dye is integrated into the fibre, making the colour an integral part of the fabric. This quality enables the fabric to endure wear, fading, and repeated washings without losing its intensity, resulting in products that last a long time.
Cost efficiency:
Dope dyeing is expensive initially but reduces overall production costs. It eliminates post-dyeing processes such as washing and drying, making it cost-effective for companies producing large volumes of uniform-coloured fibres like carpet manufacturers.
Environmental Benefits:
Dyeing fabric using the dope-dyeing method has important environmental benefits and helps make the textile industry more sustainable. By adding the dye to the fibre during manufacturing, dope-dyed fabrics use less water, eliminate the need for additional rinsing after dyeing, require fewer chemicals, and have lower energy needs compared to traditional dyeing methods. These eco-friendly practices minimize pollution, save resources, and reduce the carbon footprint of textile production. As a result, dope-dyed fabrics offer a sustainable choice without compromising quality or performance, making them a greener option for manufacturers and consumers.
End Uses of Dope Dyeing:
Apparel Industry:
The outdoor clothing brand Patagonia utilizes dope-dyed polyester in many of its products, such as the Men’s Better Sweater® Jacket. This jacket offers vibrant colour, durability, and aligns with Patagonia’s sustainability commitment by reducing water and energy consumption during production.
Nike uses dope-dyed fibres in their performance wear, such as the Nike Pro line, like the Pro Hyper Warm tights, benefiting from excellent colour fastness and environmental benefits.

Automotive Industry:
Both Tesla and BMW use dope-dyed nylon in their car interiors for seats and upholstery to maintain vibrant colours and resist fading from sunlight exposure. This material provides high durability and colour retention, especially in high-touch areas like seats and door panels.
Home Textile:
Mohawk Industries uses dope-dyed nylon for their SmartStrand® carpet line, known for stain resistance and colourfastness. Shaw Floors uses dope-dyed fibres in their Bellera® High-Performance Carpet for long-lasting colour and durability in home environments.
There are several other uses of dope-dyed fibres and fabric in Technical textiles, Outdoors and Activewear, etc
Dope dyeing is a revolutionary process in the textile industry that offers numerous benefits over traditional dyeing methods. It enhances colour fastness, reduces environmental impact, and improves cost efficiency. Understanding this process is crucial for engineering students aiming to innovate in textile manufacturing.




very nice blog post thanks