What Burn Out AOP?
Cotton and other cellulosic fibers are destroyed by strong mineral acids or their acid salts. This procedure is sometimes referred to as “Burn Out”. A cotton / polyester blended fabric can be printed with a print paste containing the burn out chemicals, and after fixation, the cotton portion is destroyed and only the polyester remains. This allows a patterned lacey design to be imparted to the fabric. It also is possible to incorporate a disperse dye in the burn out paste and dye the polyester during the burn out phase. This process is very corrosive and requires special screens and special care in handling.
BURN OUT AOP TECHNOLOGIES :
- Other names – Devour process, Corrosion process, transparency process, carbonization printing
- Flat bed screen printing/Rotary Screen Printing
- Acids instead of colours
- Can be done only on some selected fabrics ( cellulose & synthetic blend or cellulose & cotton blend)
- best composition- 60% polyester and 40% cotton fabric or vice versa; CVC & PC fabrics.
- Common chemical use – Sulphuric acid, mixed into a colourless print paste
BURN OUT AOP Machine Overview :
For Burn out AOP, Flat bed and rotary AOP machines. Here we are discussing Rotary machines here..
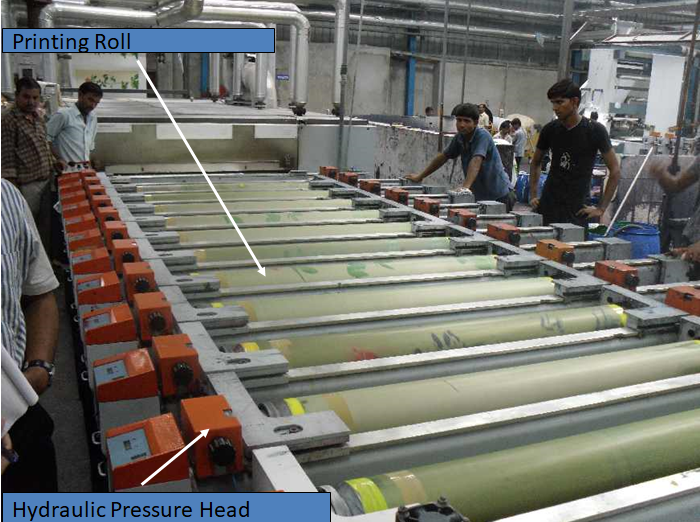
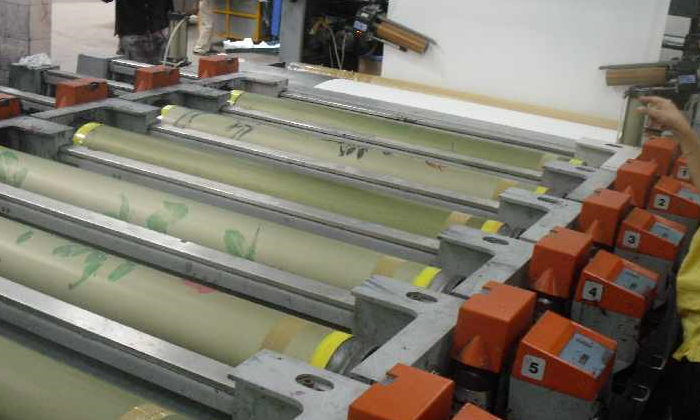
ROTARY PRINTING M/C :
- One rotary print roll is used to print burn out AOP.
- Printing roll pressure is controlled by hydraulic pressure head.
- Printing paste is pumped in to the rotary rolls through pipes.
- The printing paste is then spread over on the fabric through blade placed inside the roll.
- The fabric is then forwarded to the heated segment maintained @ 85-90 degree where the printing paste is dried up.
- The fabric is then collected at trolley placed at the end of rotary m/c


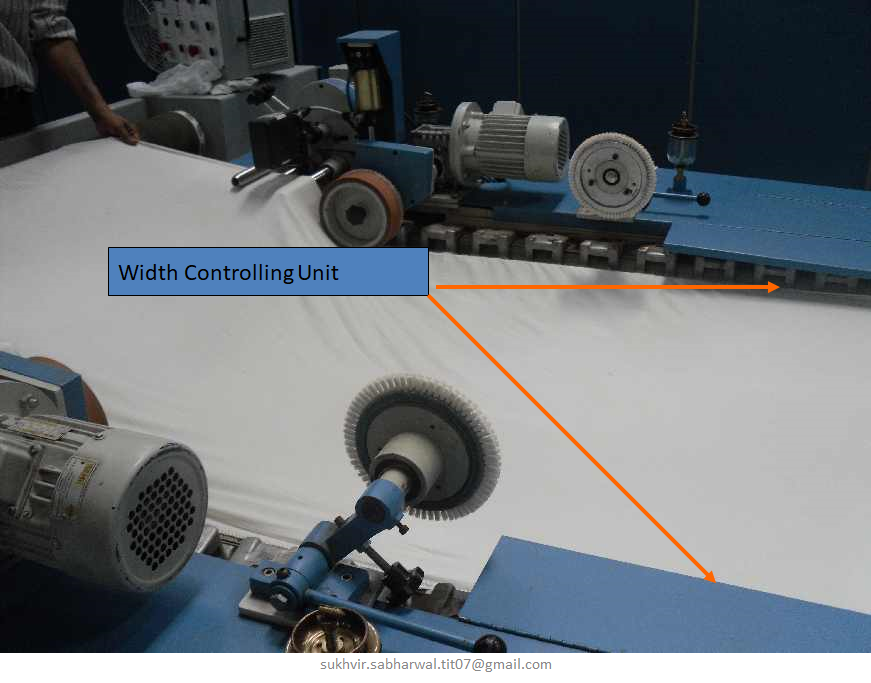
CLOSED STENTER :
- This m/c is the heart of any dyeing/printing mill.
- Final width of fabric is adjusted by this m/c.
- Softener is being applied by his m/c.
- This m/c consists of 2parts
–Dyeing tub with mangle
–Heated chambers ( 8-12)

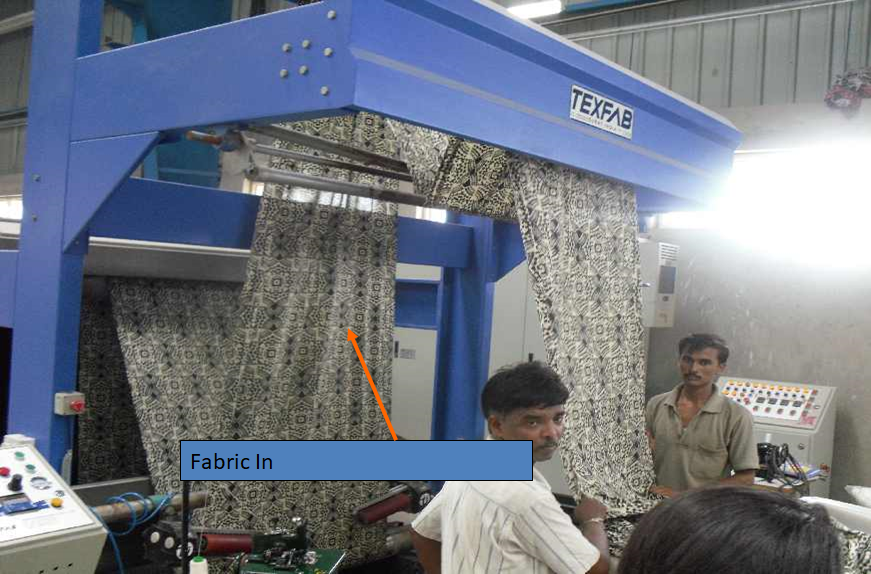
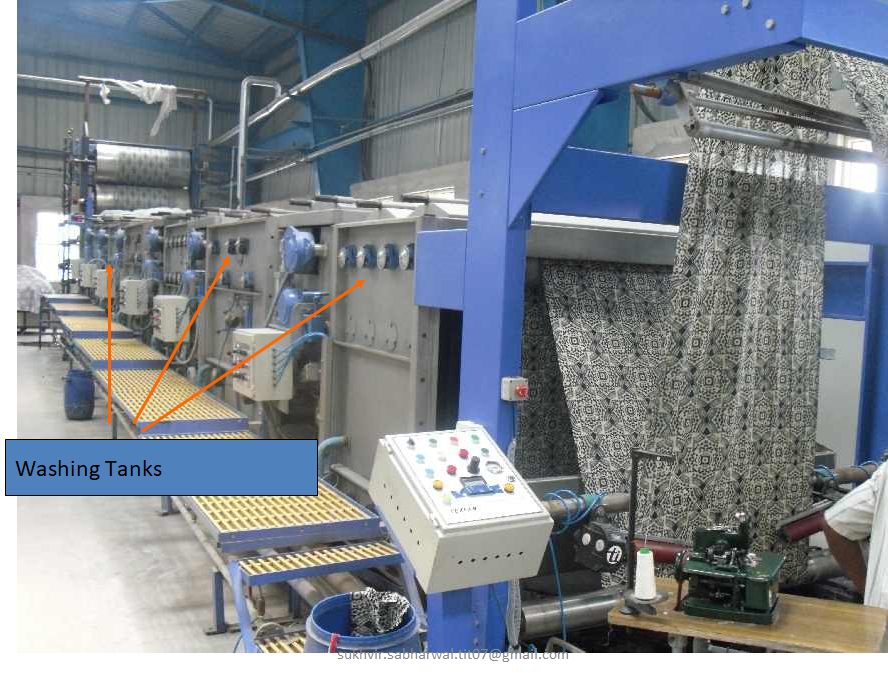
CONTINIOUS WASHER:
- This m/c is used for Discharge & Procian prints & Burn Out Print.
- The fabric is washed to extract the residual paste from the surface of fabric.
- This m/c consists of several bath tubs containing cold & hot water.
- Water is changed after every 1000 mtrs to minimize the tinting of corrosion of Acid.


Chemical requirements:
Below are the chemicals used for Burn Out AOP.
1.Sodium bisulphate
2.Synthrapol
3.Guar gum (thickener)
4.Soda Ash
5.Glycerine
Steps to be followed for Burn Out AOP:
1.Prepare thickener paste – take water in a blender and gradually add the guar gum. Continue blending till it is smooth
2.Next add sodium bisulphate to water for burn-out paste
3.When acid is dissolved, add to it the glycerine(hygroscopic) and the above prepared thickener paste and blend well
4.Prepare the padded printing surface
5.Apply the burn out paste by machine
- Allow the fabric to dry through Stenter
- When dried, it is washed by continuous wash machine.
- After wash it is again dried & make ready fabrics for dyeing.
Precautions & instructions:
1.Mix the thickener paste a few hours, or even the day before you need to use
2.Make the burn-out paste just before you are ready to use it.
3.The best paste penetration is achieved by screen printing, followed by stencilling, and then freehand applications
4.When working on silk/rayon velvet, it is best to print on the back side of the fabric rather than the pile
5.Don’t overheat the burn-out areas to a black colour, otherwise you run the risk of permanently discolouring the fabric.
6.While working with sodium bisulphate it is important to wear a dust/mist respirator, rubber gloves, safety goggles, and an apron or old clothes. Avoid contact with skin or eyes
Conclusion Discussion :
⮚Costly
⮚When fixation temperature is varied slightly, big colour variation occurs and residues can’t be removed off easily
⮚Printing paste when used on next day will not give a smooth finishing (excess=waste)
⮚Excess time / temperature may cause yellowing in unprinted areas
⮚Risky acids – skin damage